Dental care
Conservative care

It is important to see a dentist at least once a year for an oral check-up.
Thus, if there are cavities, simple solutions can be provided (care and prevention), a cleaning will be performed to remove plaque and tartar. Advice will be given to improve brushing, and additional care may be recommended if needed.
Prophylaxis
Prophylaxis is defined as “all the means put in place to prevent the occurrence of a disease”.
It prevents the appearance of cavities and decay and aims to maintain the results of dental care. The decay, loosening and loss of teeth that can result are not inevitable. If today, the clinical examination of your mouth reveals a satisfactory state and that your oral condition does not present any symptoms commonly encountered in dentistry, this state of health remains precarious.
The statistics are explicit: only 5% of the population will not experience tooth disease. In our dental office, all the measures are taken to prevent the appearance of caries or periodontal disease (decay) and to stop its evolution and aggravation.
Consequently, a prophylactic follow-up program is proposed to you to avoid the appearance and development of oral bacterial diseases. Prophylactic care replaces traditional scaling, the results of which are largely insufficient to prevent decay and protect against cavities.
tooth Decay
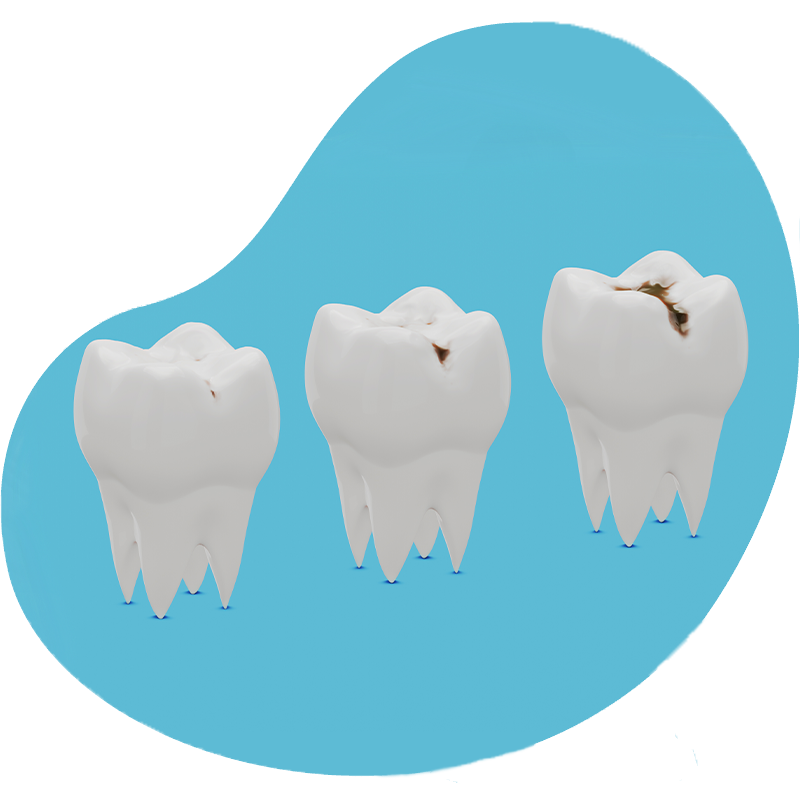
Tooth decay is an infectious disease that can affect a tooth more or less seriously depending on its stage of development. The enamel of the tooth is the first to be affected, in fact, since it covers the tooth, it will be the first visible sign, then a cavity forms in the tooth and the decay spreads in depth.
If the cavity is left untreated, the hole will enlarge and the decay may reach the dentin (layer under the enamel). Pain starts to occur, especially with hot, cold or sweet foods. The decay can then reach the pulp of the tooth and at this level, we talk about toothache. Finally, in the last stage, a dental abscess can appear when the bacteria attack the ligament, the bone or the gum.
How to prevent cavities from forming?
The best way to prevent cavities is to practice good oral hygiene:
- EDaily tooth brushing (3 times a day if possible)
- EUse of brushes or wire for the interdental spaces.
- EAnd finally, an annual visit to your dentist.
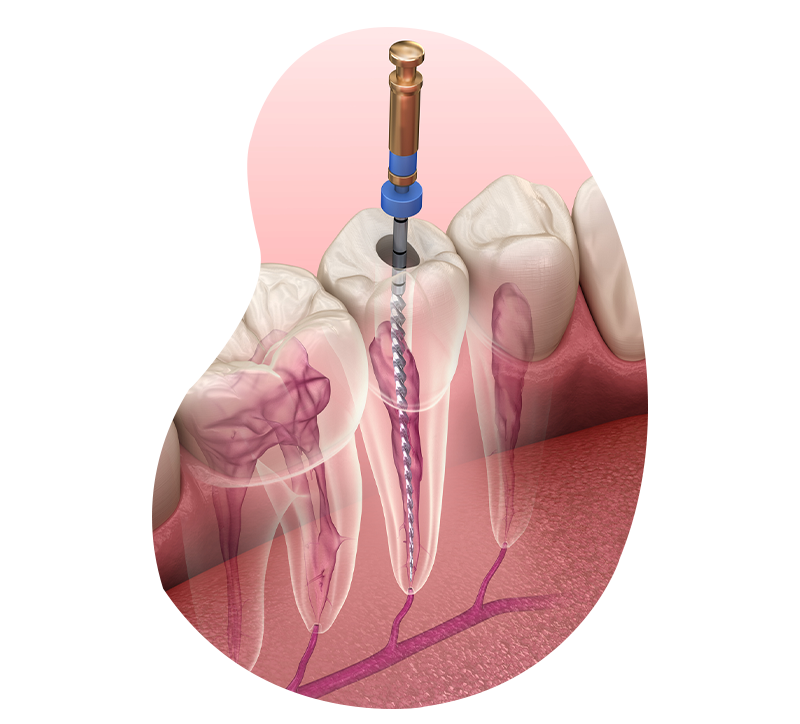
Endodontic treatment
Endodontics is the discipline that treats diseased roots and the resulting infections. It is a meticulous exercise that requires 3D imaging for diagnosis and an operating microscope during treatment.
Endodontics can be separated into three techniques
- EInitial "devitalization" treatment
- ERetreatment of an already devitalized and infected tooth
- ESurgical endodontics, which consists of surgically removing a portion of the infected root
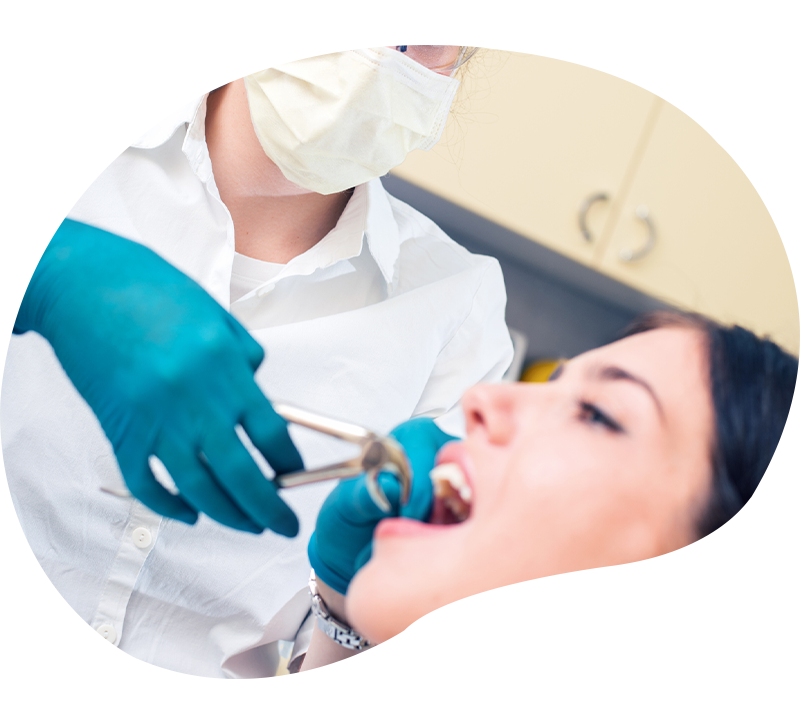
Dental extraction
Tooth extraction is a procedure that consists of removing a tooth. This is also called a dental avulsion.
There are two types of tooth extraction:
Simple: visible teeth, no complications
Surgical: devitalized teeth, damaged (decay…), included or inaccessible
The procedure is performed under local anesthesia
Causes of a dental extraction
- EAdvanced stage of caries
- EBone tissue disease
- EPresence of an abscess
- ELack of space
- ETrauma to the tooth
What happens next?
The consequences can change from one person to another. It is advisable to respect the prescriptions and the instructions given in postoperative. It is recommended:
- EIn case of bleeding: to bite on compresses during 15min and to renew the operation if necessary
- ENot to smoke for a few days
- EDo not spit, rinse, or rinse your mouth for the first 24 hours so that the blood clot can form properly to initiate healing.
- EAvoid eating and drinking too hot for the first 24 hours
- ETo reduce inflammation, apply an ice pack
- EAfter the first 48 hours, a swelling or a hematoma may occur but rest assured, it will gradually fade.
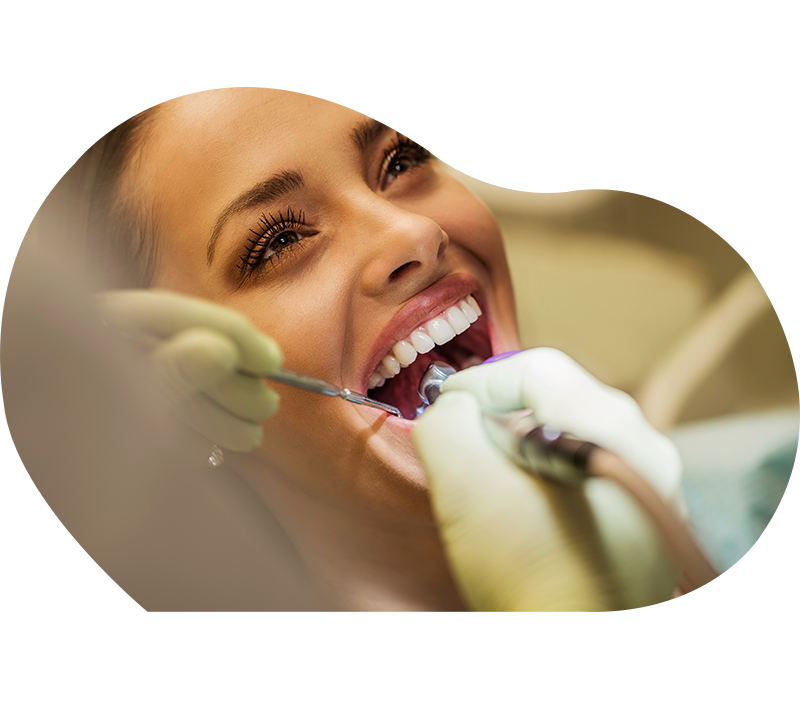
Scaling
With time, the teeth lose their brightness. In addition to tartar, external factors come to tarnish the color of a dentition: consumption of tea, coffee, cigarettes…
Tooth tartar is formed due to the presence of minerals in the saliva: calcium and phosphates and bacterial plaque present on the teeth. A concentration of this dental tartar is more regularly observed behind the teeth of the lower jaw, directly in contact with the tongue and saliva.
How does tartar form?
After each meal, a thin film of food debris and numerous bacteria forms on the surface of the teeth: this is dental plaque. If it is not removed on a very regular basis by effective brushing, the plaque mineralizes and hardens to form tartar which is very sticky. Because tartar is porous, many microbes can lodge in it, which can lead to the development of cavities or gum disease.
Why a scaling?
Regular scaling, combined with professional cabinet cleaning and effective brushing, will remove the yellowing marks. Scaling restores the aesthetic appearance of the teeth. In addition, tartar removal helps to recreate a healthy environment for teeth and gums, reinforces oral hygiene and prevents the onset of many gum and periodontal diseases.
Technique
Scaling is done manually by scraping off the scale film with instruments called curettes or with an ultrasonic device to remove all deposits. These two methods can be complementary. Scaling is completed by polishing the tooth surfaces with brushes mounted on a rotating instrument and impregnated with a polishing paste.
