Periodontics
Periodontal disease
Periodontal diseases are bacterial (microbial) infections that affect and destroy the tissues that surround and support the teeth (the periodontium). The tissues involved are the gum, the attachment fibers (ligament or desmodont) and the bone that supports the teeth.
Periodontal diseases represent, with dental caries, the main infections of the oral cavity.
The different stages of periodontal disease
The main symptoms and warning signs: periodontal disease is associated with significant inflammation and is therefore marked by red, swollen gums and bleeding when brushing. The main symptoms are also tooth loosening, mobility, displacement or the appearance of a gap between the teeth. Bad taste or bad breath may also persist.
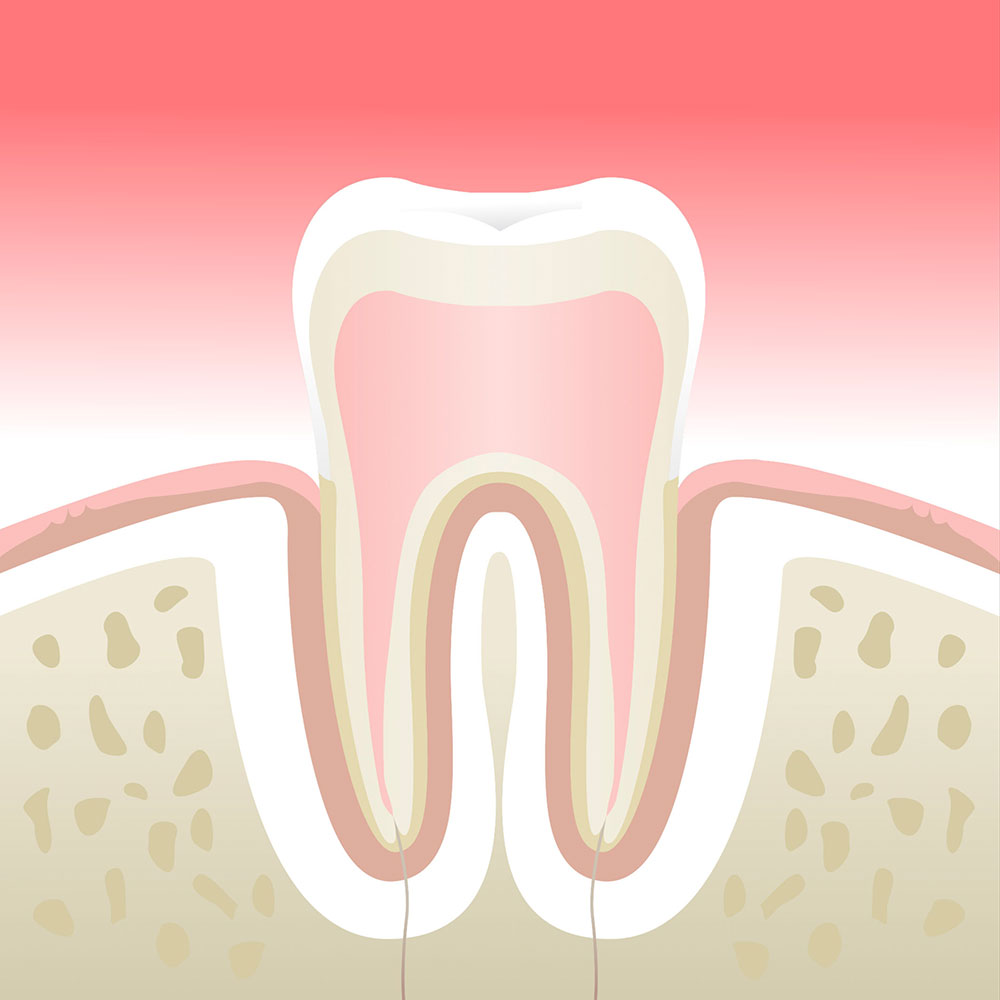
Gingivitis
To maintain healthy teeth, it is essential to also ensure the health of your gums and to remove subgingival tartar deposits.
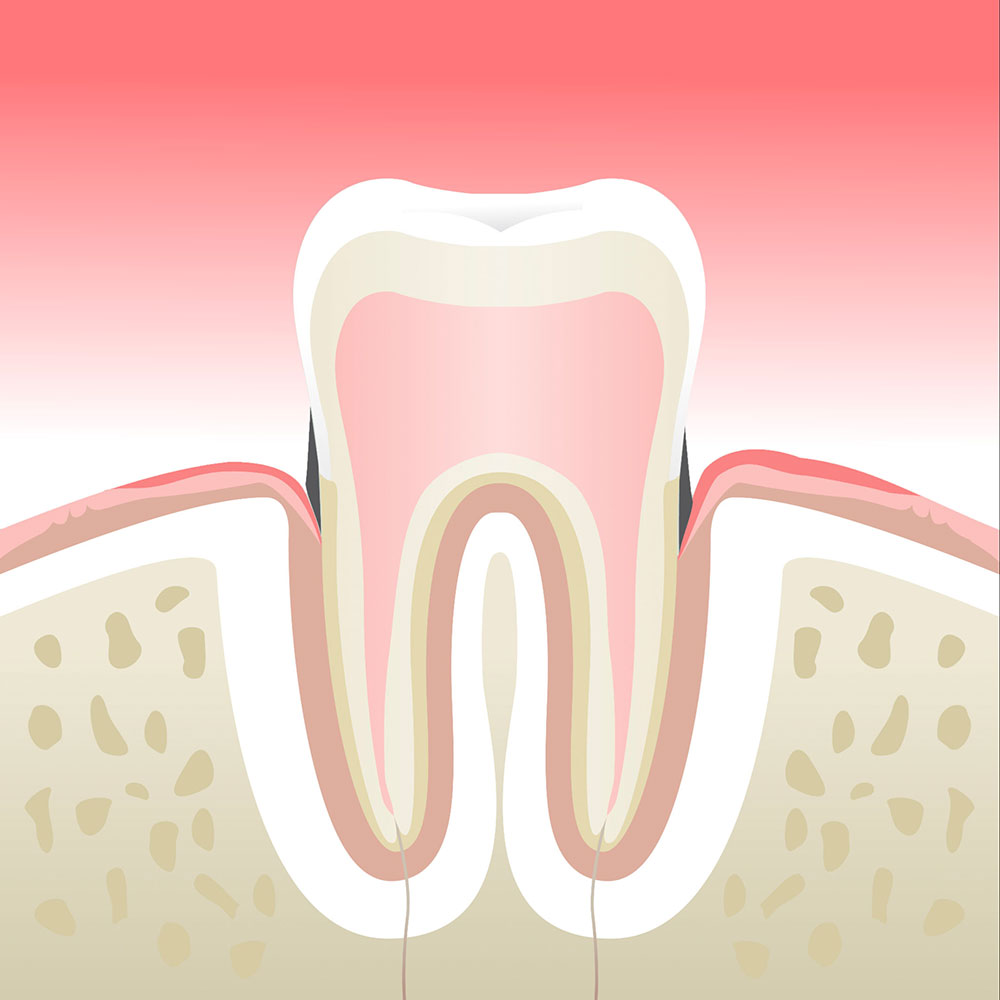
Early periodontitis
Untreated inflammation can cause lasting damage to your teeth. To prevent this from happening, we put in place appropriate treatments to stop the process and preserve the long-term health of your teeth.
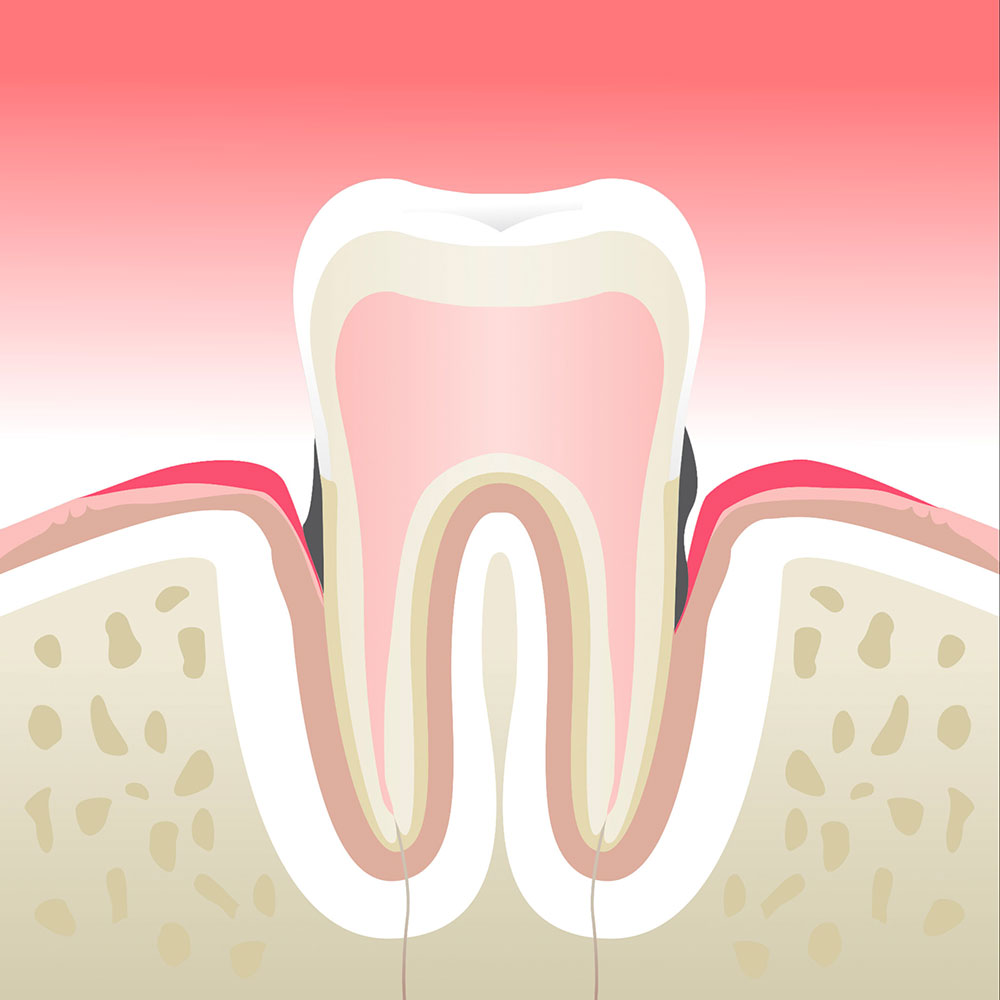
Moderate periodontitis
Periodontal diseases or periodontitis are bacterial infections that manifest themselves by gingival bleeding, gum retractions and bone loss around the tooth that can cause tooth mobility.
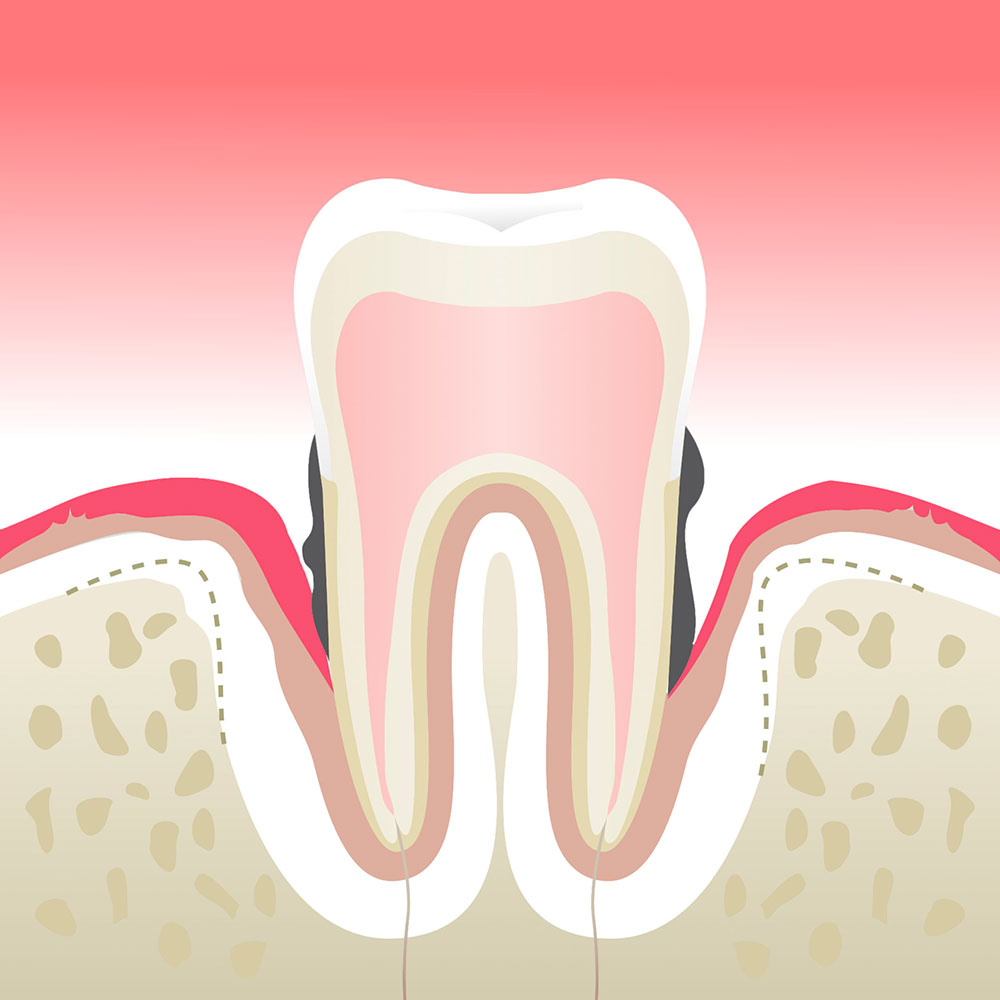
Advanced periodontitis
Plaque and tartar are the triggers of periodontal disease because they support the bacteria that cause it.
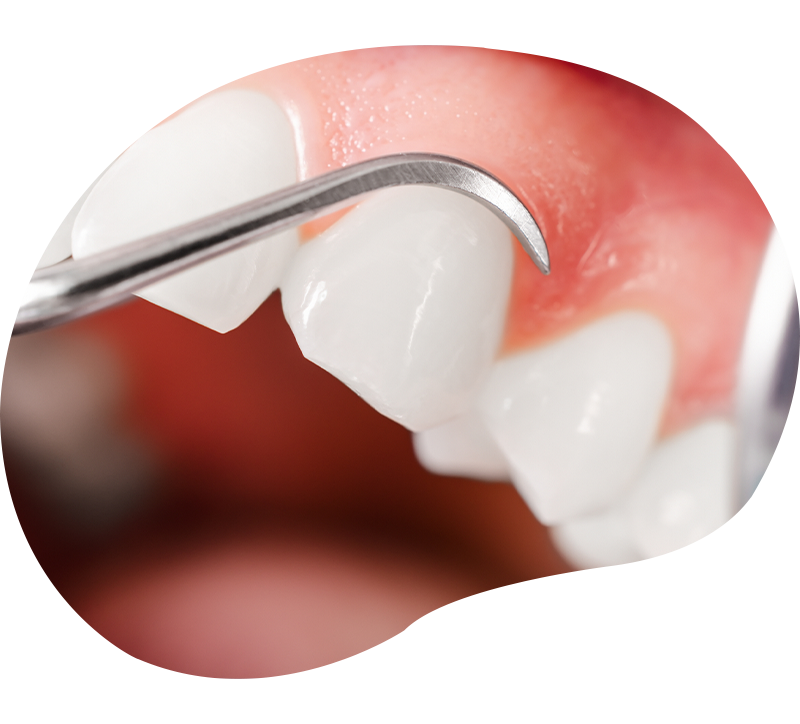
Periodontal sanitation
Periodontal sanitation is a non-surgical procedure to control periodontal infection. It consists of a mechanical debridement of the bacterial biofilm, using ultrasound or curettes.
Periodontal sanitation procedures
- EDescaling
- ECurettage / debridement of periodontal pockets using curettes and/or ultrasound
- ESurfacing
- EAntiseptic irrigation
- EAntifungal mouthwash if necessary
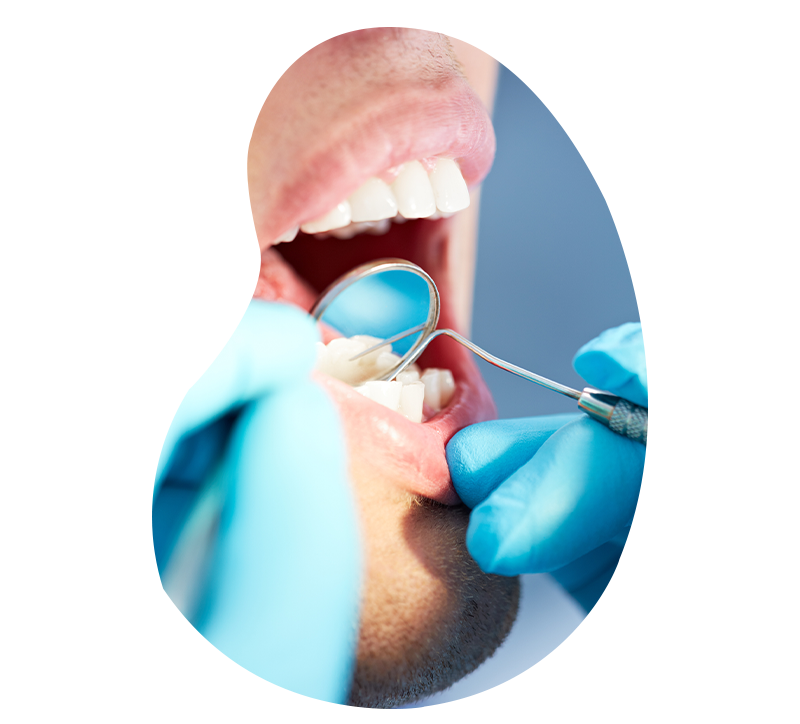
Root planing
Description of root planing
Root planing or curettage is a technique that can slow down or stop the evolution of periodontitis (periodontal disease). This method is generally very effective and not very aggressive.
Purpose of root planing
The purpose of root planing is to remove plaque and tartar that has accumulated under the gums, on the roots of the tooth. This technique is performed mainly on people with periodontitis. It consists in lifting the gum, eliminating the dental plaque by picking the pockets, spaces which were created between the gum and the tooth.
How does root planing work?
Root planing is a non-surgical technique performed under local anesthesia, i.e. by blocking the sensation of pain in the mouth.
This operation is performed with a curette, a tool used to scrape the tooth, or with ultrasonic devices whose vibration will remove tartar and plaque, i.e. accumulated bacteria.
In general, 2 to 4 sessions are necessary to deeply cleanse the tissues. These sessions are performed at short intervals to limit the risk of reinfection.
